Difference between revisions of "High-level Concepts v0.2"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
*Participant characteristic (phenotype) | *Participant characteristic (phenotype) | ||
**<font style="color:blue">Baseline characteristic</font> | **<font style="color:blue">Baseline characteristic</font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
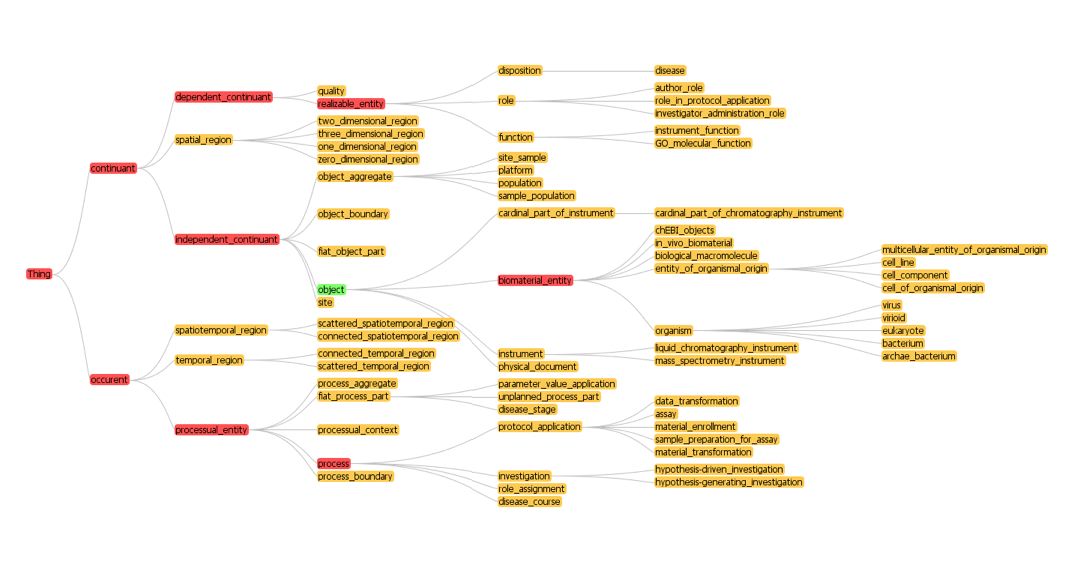
| + | ==High-Level Structure from BFO-OBI== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:High Level BFO_OBI.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 15:02, 1 May 2007
High-Level Concepts version 0.2
Initial High-level Concepts in black font
Additions from Simona in blue font
Additions from Richard in green font
- Events
- Periods
- Study phases
- Protocol phases
- Sequence of events
- Study designs
- Descriptive research – research in which the investigator attempts to describe a group of individuals based on a set of variable in order to document their characteristics
- Case study – description of one or more patients
- Developmental research – description of pattern of change over time
- Normative research – establishing normal values
- Qualitative research – gathering data through interview or observation
- Evaluation research – objectively assess a program or policy by describing the needs for the services or policy, often using surveys or questionaires
- Exploratory research
- Cohort or case-control studies – establish associations through epidemiological studies
- Methodological studies – establish reliability and validity of a new method
- Secondary analysis – exploring new relationships in old data
- Historical research – reconstructing the past through an assessment of archives or other records
- Experimental research
- Randomized clinical trial – controlled comparison of an experimental intervention allowing the assessment of the causes of outcomes
- Single-subject design
- Sequential clinical trial
- Evaluation research – assessment of the success of a program or policy
- Quasi-experimental research
- Meta-analysis – statistically combining findings from several different studies to obtain a summary analysis
- Randomized clinical trial – controlled comparison of an experimental intervention allowing the assessment of the causes of outcomes
- Descriptive research – research in which the investigator attempts to describe a group of individuals based on a set of variable in order to document their characteristics
- Research types
- Randomized Clinical Trial
- Methods
- Stakeholders
- Participants
- Investigators
- Monitors
- Sponsors
- Populations
- Screened population
- Recruited population
- Eligible population
- Enrolled population
- Randomized population
- Analysed population
- Crossover population
- Subgroup population
- Variables
- Independent variable
- Intervention
- Procedure
- Device implantation
- Drug treatment
- Placebo treatment
- Sham procedure
- Usual care
- Counseling
- Cointervention
- Intervention
- Dependent variable (responding variable)
- Outcome
- Primary outcome
- Secondary outcome
- Adverse event/Side effect
- Ancillary outcome
- Outcome
- Independent variable
- Digital and paper artifacts
- Protocol
- Intended protocol
- Executed protocol
- Protocol application
- Assessments
- Experimental assays
- Observations
- Physical exam
- Interview
- Self-assessments
- Data analysis
- Data partitioning
- Data transformation
- Data pooling
- Data summarization
- Reliability
- Correlation
- Specimen processing
- Procurement
- Specimen partitioning/purification
- Specimen storage
- Assessments
- Measurement scale
- Nominal
- Ordinal
- Interval
- Ratio
- Participant characteristic (phenotype)
- Baseline characteristic